In fact, besides build management, CMake can also handle testing and creating installation packages. The packaging feature is supported by the CPack module1, which can generate suitable installers for different platforms.
1. Qt Program CMake Configuration
Taking the previously written QML program as an example, the CMakeLists.txt configuration file is written as follows. The packaging.cmake file included at the end defines information related to packaging configuration.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.16)
set(PROJECT_NAME sample)
project(${PROJECT_NAME} VERSION 0.1 LANGUAGES CXX)
set(EXECUTABLE_NAME ${PROJECT_NAME}_app)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
find_package(Qt6 REQUIRED COMPONENTS Quick)
if(Qt6_FOUND)
message(STATUS "Qt6 found: ${Qt6_DIR}")
else()
message(FATAL_ERROR "Qt6 not found!")
endif()
qt_standard_project_setup(REQUIRES 6.8)
qt_add_executable(${EXECUTABLE_NAME}
main.cpp
)
qt_add_qml_module(${EXECUTABLE_NAME}
URI ${PROJECT_NAME}
VERSION 1.0
QML_FILES
Main.qml
)
# set static linking for MSVC
if(MSVC AND (${VCPKG_TARGET_TRIPLET} MATCHES "static"))
message(STATUS "Configuring for MSVC static linking")
set_property(TARGET ${EXECUTABLE_NAME} PROPERTY
MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY "MultiThreaded$<$<CONFIG:Debug>:Debug>")
endif()
set_target_properties(${EXECUTABLE_NAME} PROPERTIES
# MACOSX_BUNDLE_GUI_IDENTIFIER com.example.${EXECUTABLE_NAME}
MACOSX_BUNDLE_BUNDLE_VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION}
MACOSX_BUNDLE_SHORT_VERSION_STRING ${PROJECT_VERSION_MAJOR}.${PROJECT_VERSION_MINOR}
MACOSX_BUNDLE TRUE
WIN32_EXECUTABLE TRUE
)
target_link_libraries(${EXECUTABLE_NAME}
PRIVATE Qt6::Quick
)
include(GNUInstallDirs)
install(TARGETS ${EXECUTABLE_NAME}
BUNDLE DESTINATION .
LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}
RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_BINDIR}
)
if(MSVC AND (${VCPKG_TARGET_TRIPLET} MATCHES "static"))
message(STATUS "Linking static MSVC runtime, skipping install of MSVC runtime DLLs")
else()
message(STATUS "Configuring install of runtime dependencies")
set(deploy_tool_options_arg "")
if(APPLE)
set(deploy_tool_options_arg --hardened-runtime)
elseif(WIN32)
set(deploy_tool_options_arg --no-compiler-runtime)
endif()
qt_generate_deploy_qml_app_script(
TARGET ${EXECUTABLE_NAME}
OUTPUT_SCRIPT deploy_script
MACOS_BUNDLE_POST_BUILD
NO_UNSUPPORTED_PLATFORM_ERROR
DEPLOY_USER_QML_MODULES_ON_UNSUPPORTED_PLATFORM
DEPLOY_TOOL_OPTIONS ${deploy_tool_options_arg}
)
install(SCRIPT ${deploy_script})
install(CODE [[
if("$ENV{VCPKG_TARGET_TRIPLET}" STREQUAL "")
find_program(QMAKE qmake6 HINTS $ENV{PATH})
if(NOT QMAKE)
message(FATAL_ERROR "qmake not found in PATH")
else()
message(STATUS "qmake found: ${QMAKE}")
cmake_path(GET QMAKE PARENT_PATH QT_BIN_DIR)
message(STATUS "qmake bin dir: ${QT_BIN_DIR}")
endif()
else()
set(QT_BIN_DIR "$ENV{VCPKG_ROOT}/installed/$ENV{VCPKG_TARGET_TRIPLET}/bin")
if(NOT EXISTS ${QT_BIN_DIR})
message(FATAL_ERROR "qmake bin dir not found: ${QT_BIN_DIR}")
endif()
endif()
file(GET_RUNTIME_DEPENDENCIES
RESOLVED_DEPENDENCIES_VAR RESOLVED_DEPS
UNRESOLVED_DEPENDENCIES_VAR UNRESOLVED_DEPS
# path to the executable files
EXECUTABLES $<TARGET_FILE:sample_app>
# directories to search for library files
DIRECTORIES ${QT_BIN_DIR}
PRE_EXCLUDE_REGEXES "system32"
PRE_EXCLUDE_REGEXES "api-ms-*"
POST_EXCLUDE_REGEXES "system32"
)
foreach(DEP_LIB ${RESOLVED_DEPS})
file(INSTALL ${DEP_LIB} DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX}/bin)
endforeach()
]])
endif()
include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/packaging.cmake)
After defining what to install in install, add packaging-related content at the end of the CMake configuration file2.
# --- packaging.cmake ---
include(InstallRequiredSystemLibraries)
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_NAME "qml_sample_install")
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION})
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_CONTACT "author_email@example.com")
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_VENDOR "author_name")
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_EXECUTABLES "${EXECUTABLE_NAME}" "${EXECUTABLE_NAME}")
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_DESCRIPTION_SUMMARY "A demo qt quick application with CMake packaging")
set(CPACK_RESOURCE_FILE_LICENSE "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/LICENSE" CACHE FILEPATH "License file")
set(CPACK_RESOURCE_FILE_README "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/README.md" CACHE FILEPATH "Readme file")
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_INSTALL_DIRECTORY "${PROJECT_NAME}")
set(CPACK_CREATE_DESKTOP_LINKS "bin/${EXECUTABLE_NAME}")
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_FILE_NAME "${CPACK_PACKAGE_NAME}-${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION}-${CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME}")
include(CPack)
2. NSIS Packaging
CPack itself does not provide a way to create installation packages; it requires other programs to package it into an executable installer. Commonly used programs on the Windows platform include NSIS3 and Inno Setup4.
First, run the cmake command to configure the build scripts and compile.
cmake -B build .
cmake --build build --config Release
Enter the build directory and run the CPack program to create a package. -G "NSIS" specifies that the package generator is NSIS5. Make sure to add the NSIS installation directory to your PATH.
$Env:PATH += ";D:\conda\envs\cpp_env\NSIS"
cd build
cpack -G "NSIS"
After completion, the generated exe installer can be found at the build/_CPack_Packages/win64/NSIS path.
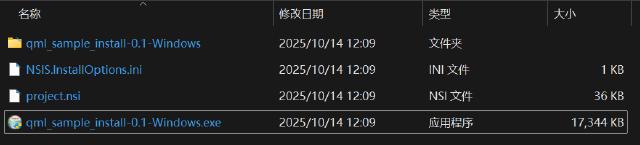

Using NSIS for packaging is only suitable for the Windows platform, and the packaged installer can be directly opened with compression programs like 7z or WinRAR, so its security is not high.
3. Inno Setup Packaging
CPack’s generator ‘INNOSETUP’6 also requires installing Inno Setup first and adding its installation path to the PATH.
$Env:PATH += ";D:\opt\Inno Setup 6"
cd build
cpack -G "INNOSETUP"
After the packaging is complete, the installation files will be generated in the build/_CPack_Packages/win64/INNOSETUP path.
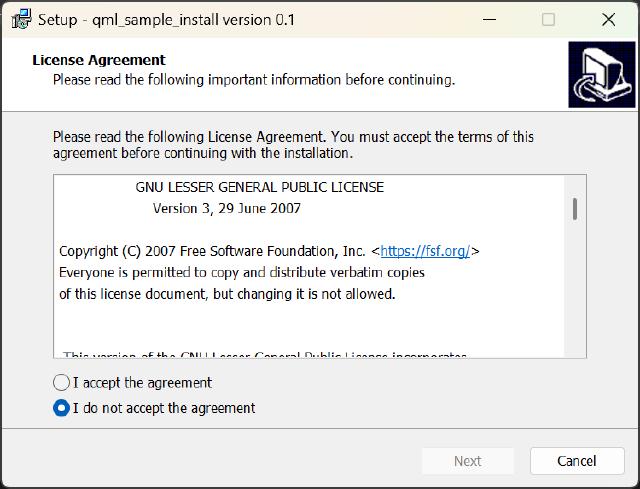
Inno Setup is also only suitable for the Windows platform. Compared to NSIS, it has some security improvements, but it can still be unpacked using specialized tools.
4. WiX Packaging
WiX7 is a packaging tool specifically developed for Windows, used to generate .msi format installation packages. The packaging tool can be downloaded from the WiX3 release page .
WiX license files only support RTF format, so you need to define CPACK_WIX_LICENSE_RTF in the CMake configuration file to specify the license file; otherwise, an error will occur when building the installer.
# --- packaging.cmake ---
...
set(CPACK_WIX_LICENSE_RTF "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/LICENSE.rtf" CACHE FILEPATH "License file in RTF format")
...
Generator selected “WIX”8.
$Env:PATH += ";D:\opt\wix314-binaries"
cd build
cpack -G "WIX"
After the packaging is complete, check the generated files at the build/_CPack_Packages/win64/WIX path.
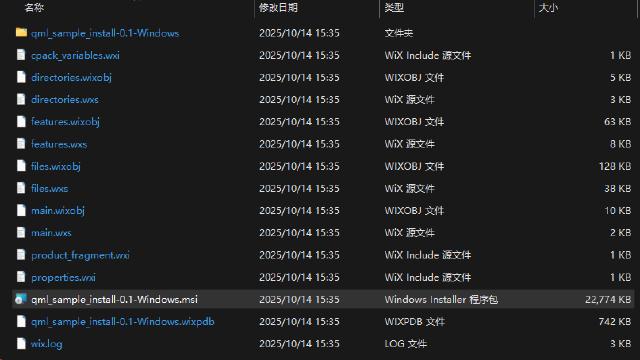
Programs packaged in this way will not leave an uninstaller in the installation directory after installation, and need to be uninstalled through the ‘Control Panel - Programs’ or ‘Settings - Apps’ interface.
5. Qt Installer Framework Packaging
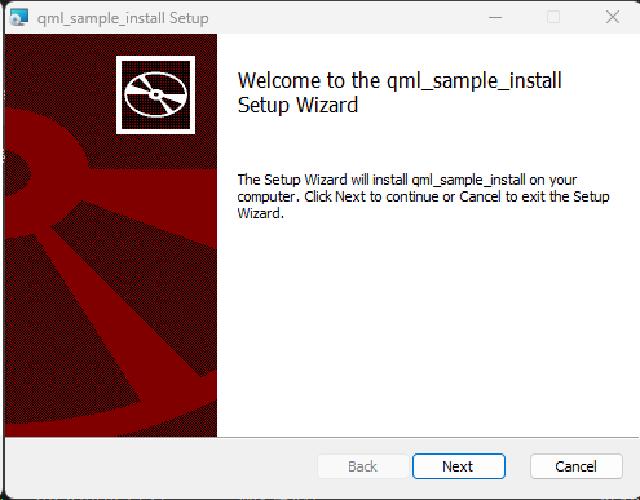
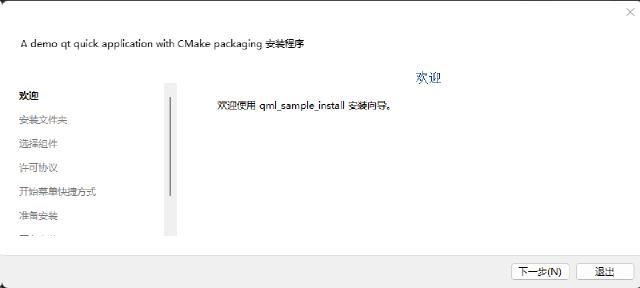
The Qt Installer Framework9 is an installation program specifically developed by Qt for packaging Qt applications, and it is suitable for all platforms supported by Qt. The Qt Installer Framework can be downloaded from the official Qt release website10.
For the CPack packaging command, choose ‘IFW’ as the generator11.
$Env:PATH += ";D:\opt\Qt\QtIFW-4.8.1\bin"
cd build
cpack -G "IFW"
After packaging on Windows, the installation files are generated in the build/_CPack_Packages/win64/IFW path.
After packaging in Linux, you can directly find the installation file in the build directory, with a .run extension added by default.
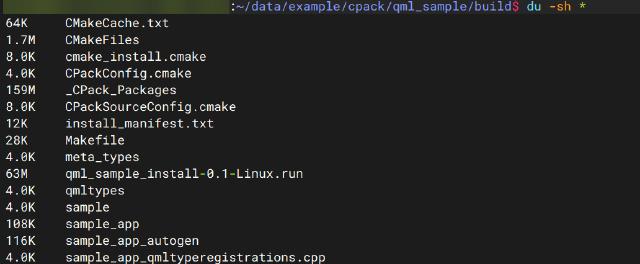
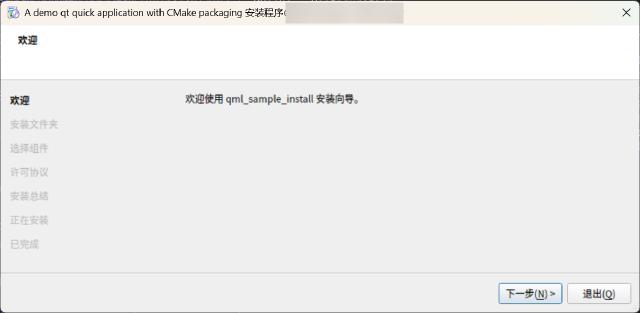
The advantage of packaging with the Qt Installer Framework is that it supports cross-platform use and maintains good consistency in the installer interface across different platforms. The disadvantage is that it cannot generate Start menu entries or desktop shortcuts, so you need to write installation scripts separately for different platforms.
6. Package DEB file
CPack supports packaging Linux binaries. Specify the DEB generator12 to create DEB packages, which are suitable for systems like Ubuntu and Debian.
cpack -G "DEB"
After packaging, the DEB package is generated directly in the build directory.
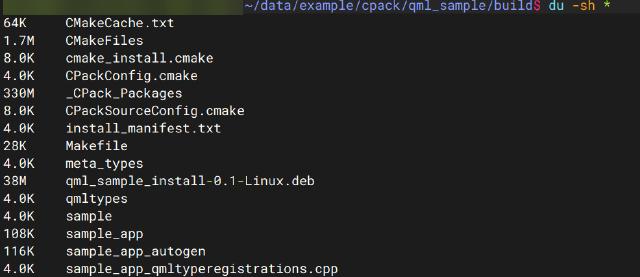
You can install it directly using the dpkg tool, or you can also install it using the apt tool.
dpkg -i path-to-package.deb
7. Package RPM file
Specify the DEB generator13 to create RPM packages, suitable for systems like Fedora, Red Hat, and SUSE.
cpack -G "RPM"
The RPM package generated by the build can be found in the build directory.
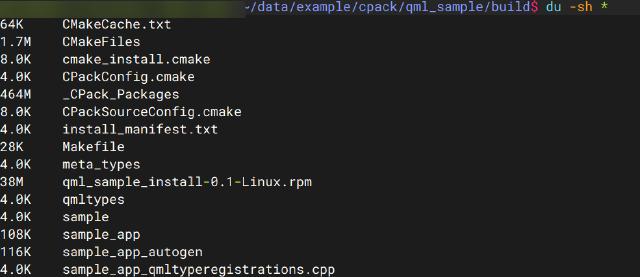
You can install it using the rpm tool, or you can use package management tools like dnf or zypper to install it.
rpm -ivh path-to-package.rpm
8. Summary
For installation packages released on Windows, it is recommended to use Inno Setup or WiX for packaging. For Linux, it is recommended to generate DEB and RPM packages separately to meet the requirements of different distributions.
If you do not consider the file size after packaging, you can use the Qt Installer Framework for packaging, which is cross-platform and offers better consistency, but you will need to write scripts yourself to create desktop icons and Start menu shortcuts.
