1. Define parameters
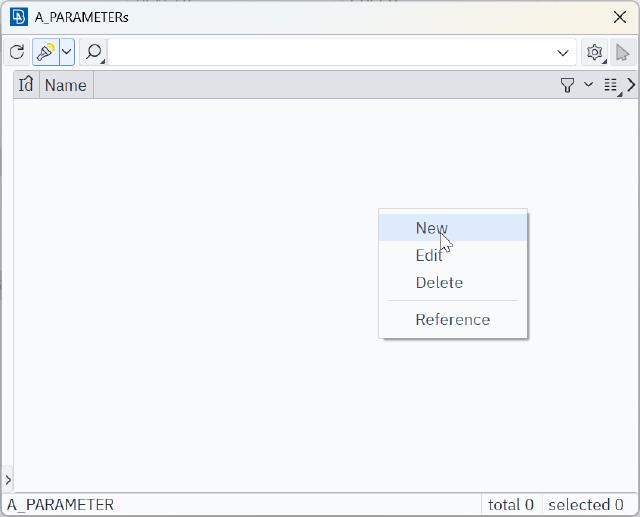
Custom parameters in ANSA are relatively simple. Right-click in the input box to open the menu and select List variables, then create a new variable in the A_PARAMETERs dialog and assign a name to that variable.
For example, here the material parameter is assigned as a custom parameter:
-
Right-click to select the
list variables.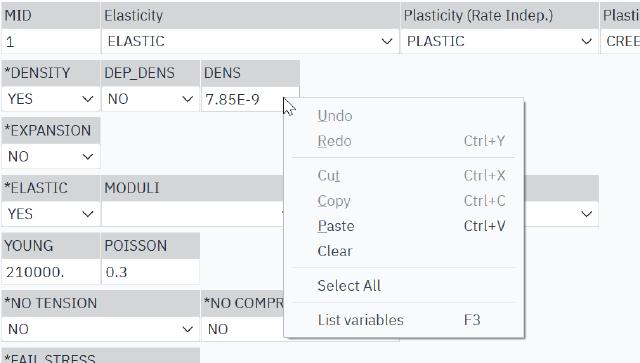
-
Create a new variable.
-
Define variable parameters.
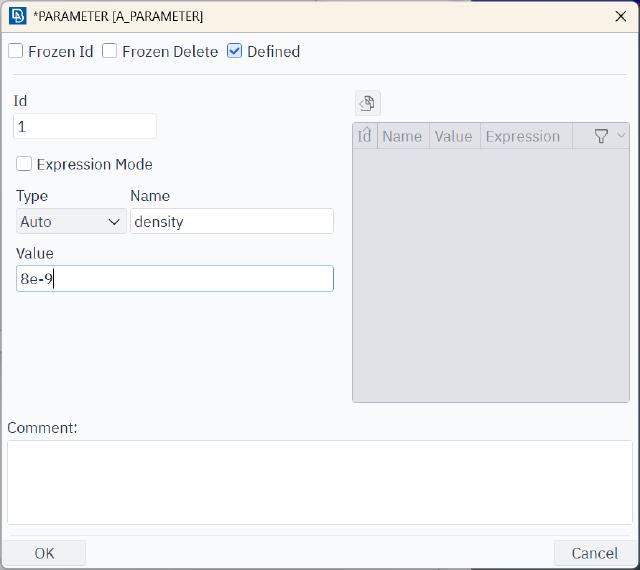
-
Assign variable.
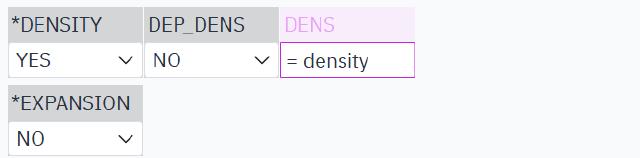
The final custom parameters can be viewed in the left panel.
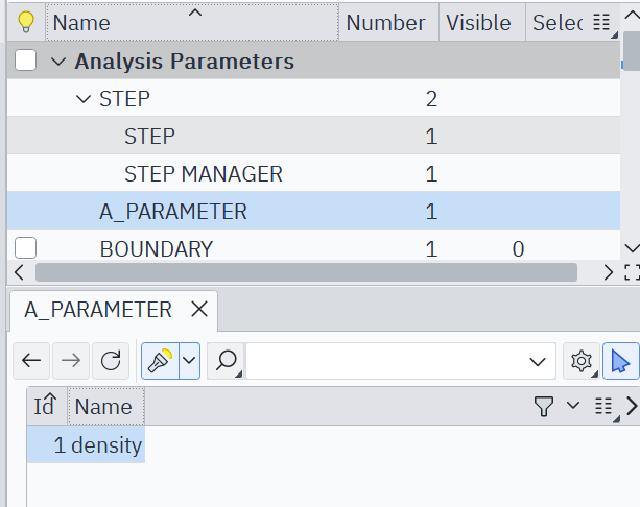
This method allows you to easily define some variables that need frequent adjustments.
If Abaqus is used as the solver, the parameters will be embedded into the .inp file.
*PARAMETER
density = 8e-9
When solving, .par and .pes files will be generated. The .pes file is the version of the .inp file expanded without parameters; the actual solution is done on the .pes file.
2. Define formula
In addition to parameters with fixed values, we can also define formulas, which will use some built-in functions. The dialog box below provides commonly used formulas, making it easier for users to look up and edit frequently used functions.
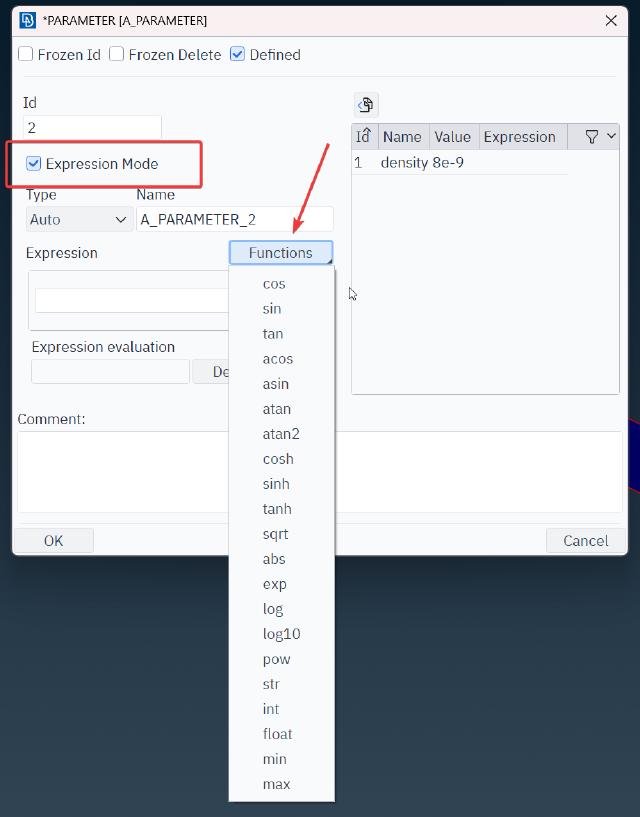
If you need to define some variable loads that are related to node or cell coordinates, you need to use some specially marked functions (see the figure below).
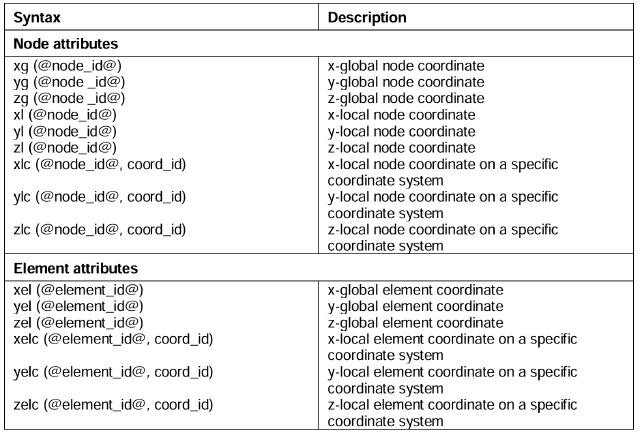
This information can be found in the PDF help documents that came with version 24 and earlier; when ANSA was updated to version 25, it switched to HTML help documents, and this information could no longer be found.
The documents also list which solvers correspond to which boundary conditions that can use these markers.
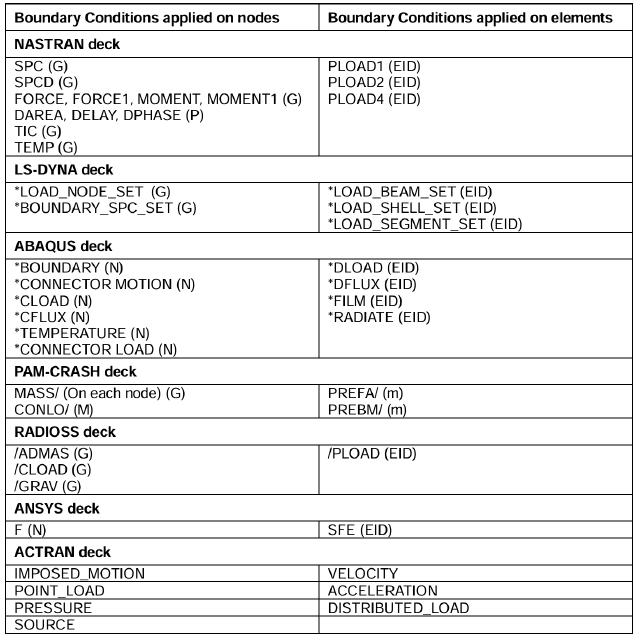
3. Example
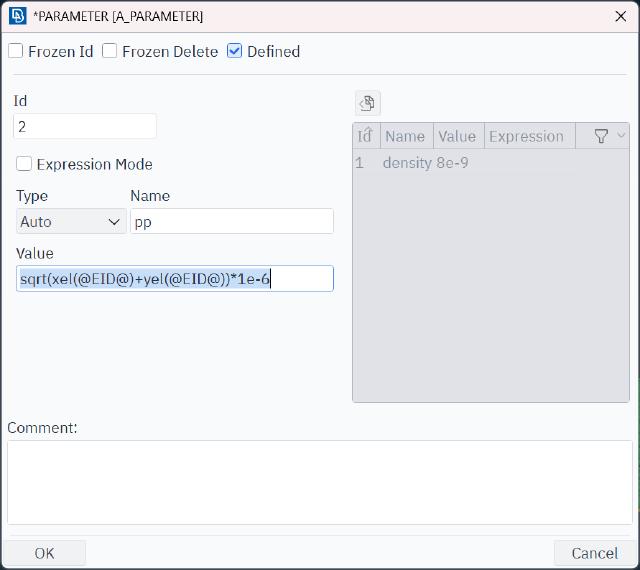
We define a non-uniform surface pressure that varies according to the coordinates, with a numerical value equal to the square root of the sum of the x and y coordinates of the cell. Please note the units: ANSA’s default length unit is mm, which corresponds to a pressure unit of MPa.
sqrt(xel(@EID@)+yel(@EID@))*1e-6
Here, the formula is defined through parameters.
Note that the load must be defined using set. You can define the formula through parameters or enter the formula directly in the dialog box.
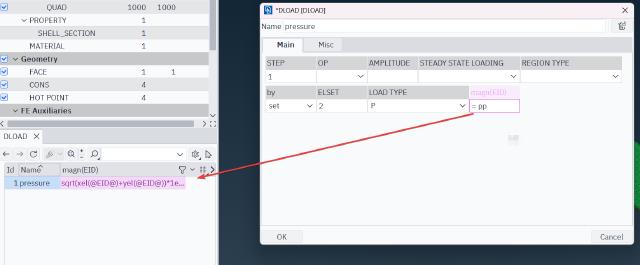
However, after setting it up, there is no visible difference in the graphics displayed in ANSA; all the vector arrows are the same size.
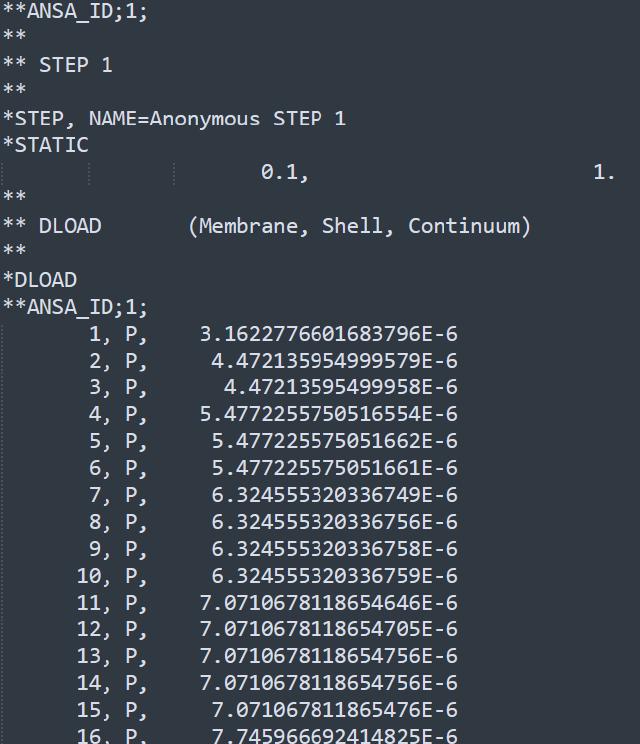
The pressure values can only be seen in the .inp file; when outputting the solution file, the variables with special marker functions have already been expanded.
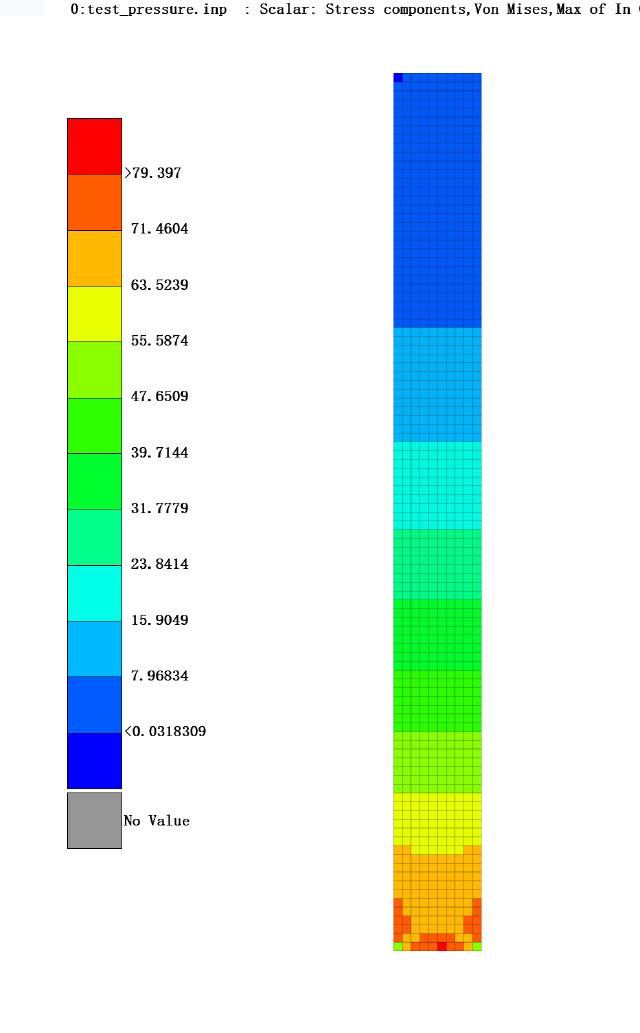
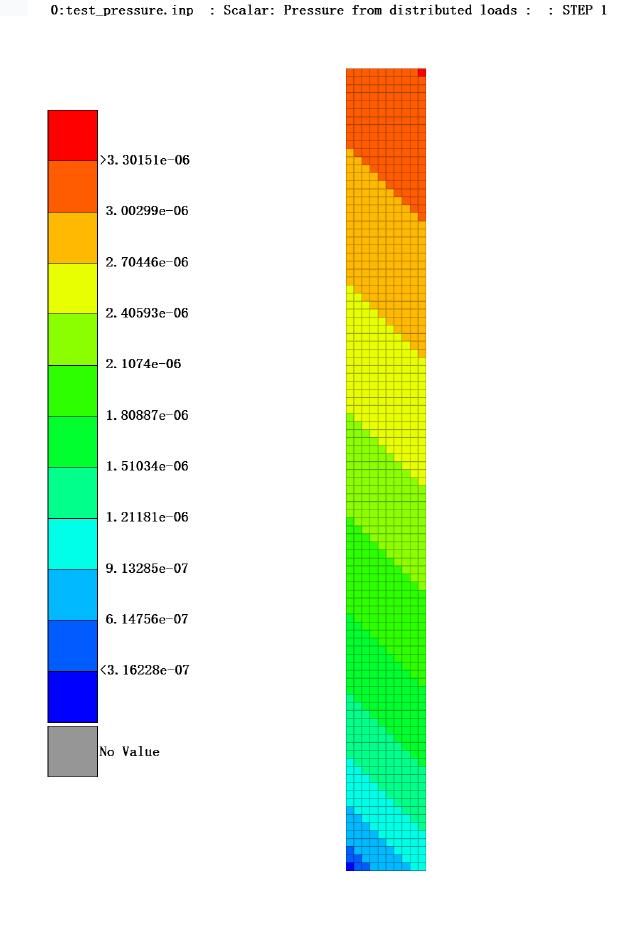
After the solution is completed, you can view the applied load distribution in META using the PDLOAD keyword.
Stress distribution of the solution results.