Recently, due to business reasons, I have been collaborating with a certain supercomputing supplier, and during the process, there were issues related to deploying Abaqus software. Although the platform’s customer service provided an installation plan, for someone like me who loves tinkering, I wouldn’t rest until I solved it myself, and I could also take the opportunity to write an article about it.
1. Platform Configuration
I won’t go into which platform it is, anyway, they didn’t pay me for advertising.
The installer used here is SIMULIA 2024, with system requirements of GLIBC>=2.281, GLIBCXX>=3.4.21, and CXXABI>=1.3.9. The latter two are easy to handle; you can temporarily bypass the restrictions by loading a higher version of libstdc.so via LD_PRELOAD. However, GLIBC involves the underlying system libraries, and unless you upgrade your distribution or recompile, there really isn’t a good workaround.
Use the following command to check the GLIBC version on the current login node.
getconf GNU_LIBC_VERSION

Note that this is the GLIBC version on the login node; the GLIBC on the compute nodes and login node, or even the distribution, may not be the same, so it needs to be confirmed with the platform.
Given the nature of these platforms, most deployment nodes are installed with CentOS 7 or the corresponding version of RHEL, and the version numbers are usually not very high, as compatibility is prioritized.
uname -r -v

2. GLIBC Switch
Fortunately, the platform I’m using has introduced a GLIBC version hot-switching feature2. Combined with Slurm, you just need to add two lines of comments at the top of the computation script, which is quite convenient.
...
#SBATCH --comment={glibcVersion:2.31} # Specify the use of glibc 2.31 environment
#SBATCH --exclusive # Exclusive node
...
As for which partition supports which GLIBC version, you can check using the whichpartition command.
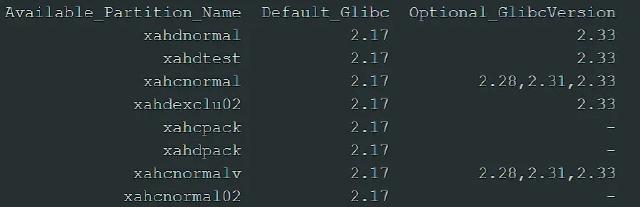
Because the GLIBC version on the login node is too low, you need to log in to a compute node and switch to a higher version of GLIBC for installation. Use the salloc command to request exclusive access to a compute node. The -p option specifies the partition of the compute node as wzhctest, -N1 specifies occupying 1 node, and -t sets the runtime to 2 hours (to avoid high charges caused by not exiting after a timeout). Other options are the same as in the sbatch script comments.
salloc -p wzhctest -N1 --ntasks-per-node=64 -q normal -t 2:00:00 --comment={glibcVersion:2.31} --exclusive
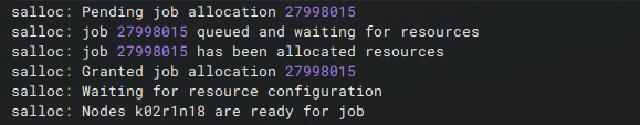
After a successful application, the job number and node list will be returned, and you can also view the node list of the applied job number through squeue. Next, we will connect to the node via SSH.
ssh k02r1n18 # k02r1n18 is the name of the node displayed above
Use getconf GNU_LIBC_VERSION to check the GLIBC version on the logged-in compute node.

3. Install Abaqus
Load a higher version GCC development environment.
module purge # Clear the currently loaded modules
module load compiler/gcc/9.3.0 # Load GCC 9.3.0
Define some environment variables to avoid errors
export DSYAuthOS_`lsb_release -si`=1
export DSY_Force_OS=linux_a64
export NOLICENSECHECK=true
At this time, directly launching the installer will still result in an error.
./StartTUI.sh
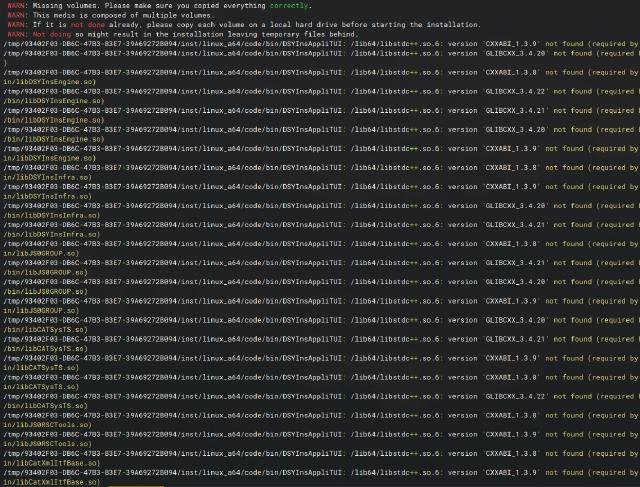
As mentioned earlier, you can temporarily bypass the restriction by specifying the environment variable LD_PRELOAD to load a higher version of libstdc.so. If you ask me where to find a higher version of libstdc.so, I can only tell you to scan your system environment on yourself.
LD_PRELOAD=/public/software/compiler/gnu/gcc-9.3.0/lib64/libstdc++.so.6.0.28 ./StartTUI.sh
Enter the installation interface normally, and at this point, you can complete the installation by referring to the previous article3.
If you encounter a problem where the Linux license server cannot start, you can consider installing the 2022 version of the SSQ license server. Both work the same way, but the SSQ license requires root permissions to install on the server. On supercomputers, regular users typically do not have root permissions, so it is recommended to contact the platform support for assistance. You can also refer to this article4 for a solution to the license server issue through separate deployment.
4. After work
After the installation is complete, remember to use the exit command to leave the compute node, and then cancel the job with scancel to avoid continuous charges.
scancel 27998015 # 27998015 is your job number and can be checked through squeue.
Create a new environment variable configuration file abaqus2024.env. It is best to place it in the installation directory for easy packaging and moving across different computing partitions.
export LICENSE_PREFIX_DIR=[install-path]/SIMULIA/License/2024/linux_a64/code/bin
export SIMULIA_COMMAND_DIR=[install-path]/SIMULIA/Commands
export PATH=$SIMULIA_COMMAND_DIR:$LICENSE_PREFIX_DIR:$PATH
export LM_LICENSE_FILE=29100@login01 # The license server is deployed on the login01 node
The reference calculation script is as follows and can be submitted via sbatch.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -J abaqus2024 # Job name
#SBATCH -p test # Partition of the compute node
#SBATCH -N 1 # Number of nodes
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=64 # Number of processes per node
#SBATCH --comment={glibcVersion:2.31}
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH -o out.%j
#SBATCH -e err.%j
module purge
module load compiler/gcc/9.3.0
module load mpi/openmpi/4.1.5/gcc-9.3.0
source /work/home/ac8ytpxsek/opt/SIMULIA/abaqus2024.env
export EXEC=abaqus
WORK_DIR=`pwd` # Current Directory
INPUT_FILE=abaqus_test.inp # Input file
job_name=`echo ${INPUT_FILE} | awk -F. '{print $1}'`
#USER_FILE=example.for # Fortran subroutine
LOG_FILE=abaqus_test.log
#########################################################
cd $WORK_DIR
env_file=abaqus_v6.env
node_list=$(scontrol show hostname ${SLURM_NODELIST} | sort -u)
mp_host_list="["
for host in ${node_list}; do
mp_host_list="${mp_host_list}['$host', ${SLURM_CPUS_ON_NODE}],"
done
mp_host_list=$(echo ${mp_host_list} | sed -e "s/,$/]/")
echo "mp_host_list=${mp_host_list}" >${env_file}
echo "mp_mpi_implementation=PMPI" >>${env_file}
echo "mp_file_system=(SHARED, LOCAL)" >>${env_file}
$EXEC job=${job_name} input=${INPUT_FILE} cpus=$SLURM_NPROCS mp_mode=MPI int
