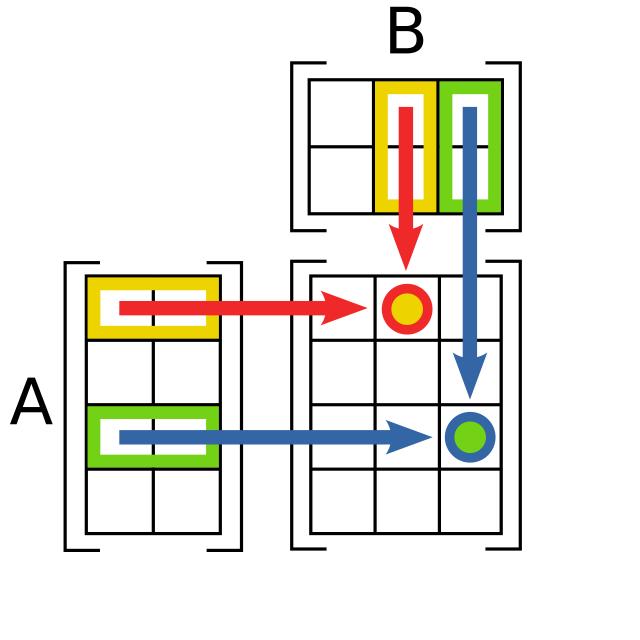
矩阵乘法运算(三)-使用MPI并行加速
MPI是一种并行计算协议,也是目前高性能计算集群最为常用的接口程序。MPI通过进程间消息进行通讯,可以跨节点调用多核心执行并行计算,这是OpenMP所不具备的。不同平台均有mpi实现,比如Windows下的MS-MPI和Intel MPI,Linux下的OpenMPI和MPICH等。
1. MPI并行加速循环计算
1.1 C实现
mpi需要对主程序接口进行初始化,建立消息广播机制;同时将需要计算的数组进行分割,广播到不同的进程中。以往这些操作都是openmp或其他并行库内部实现的,程序员不需要关心底层如何实现。但使用mpi需要程序员对每个进程的全局和局部空间进行手动分配,需要控制每个消息的广播,无疑增加了额外的学习成本。
这里将main.c文件修改如下。
#include "mpi.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
#define MIN(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b))
extern void matrix_multiply_float(int n, int rank, int size, float local_A[], float B[], float local_C[]);
extern void matrix_multiply_double(int n, int rank, int size, double local_A[], double B[], double local_C[]);
// Initialize matrix
void initialize_matrix_float(int n, float matrix[])
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
matrix[i * n + j] = rand() / (float)(RAND_MAX);
}
}
}
void initialize_matrix_double(int n, double matrix[])
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
matrix[i * n + j] = rand() / (double)(RAND_MAX);
}
}
}
// Execute matrix multiply and print results
int mpi_float(int dim, int loop_num, double *ave_gflops, double *max_gflops, double *ave_time, double *min_time)
{
int rank, size;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
// Use volatile to prevent compiler optimizations
volatile float *a, *b, *local_c;
struct timespec start_ns, end_ns;
double cpu_time, total_cpu_time;
// 计算每个进程处理的行数
int rows_per_process = dim / size;
int remainder = dim % size;
if (rank < remainder)
{
rows_per_process++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < loop_num; i++)
{
int check_indices[2];
float check_value;
// 主进程分配完整矩阵内存
if (rank == 0)
{
a = (float *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(float));
b = (float *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(float));
if (a == NULL || b == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed\n");
return 0;
}
initialize_matrix_float(dim, a);
initialize_matrix_float(dim, b);
// 生成校验值
int check_row = rand() % dim;
int check_col = rand() % dim;
check_value = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < dim; k++)
{
check_value += a[check_row * dim + k] * b[k * dim + check_col];
}
check_indices[0] = check_row;
check_indices[1] = check_col;
// 广播校验行列索引和校验值
MPI_Bcast(check_indices, 2, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Bcast(&check_value, 1, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else
{
a = NULL;
b = NULL;
MPI_Bcast(check_indices, 2, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Bcast(&check_value, 1, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
// 为每个进程分配局部矩阵空间
float *local_A = (float *)malloc(rows_per_process * dim * sizeof(float));
local_c = (float *)calloc(rows_per_process * dim, sizeof(float));
if (local_A == NULL || local_c == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed\n");
return 0;
}
// 分发矩阵 A 的行到各个进程
int *sendcounts = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
int *displs = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
int offset = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < size; p++)
{
sendcounts[p] = (p < remainder) ? (rows_per_process * dim) : ((rows_per_process - 1) * dim);
displs[p] = offset;
offset += sendcounts[p];
}
MPI_Scatterv(a, sendcounts, displs, MPI_FLOAT, local_A, rows_per_process * dim, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 所有进程都需要完整的矩阵 B
float *full_B = (float *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(float));
if (full_B == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed for full_B\n");
return 0;
}
if (rank == 0)
{
memcpy(full_B, b, dim * dim * sizeof(float));
}
MPI_Bcast(full_B, dim * dim, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
timespec_get(&start_ns, TIME_UTC);
matrix_multiply_float(dim, rank, size, local_A, full_B, local_c);
timespec_get(&end_ns, TIME_UTC);
cpu_time = (end_ns.tv_sec - start_ns.tv_sec) + (end_ns.tv_nsec - start_ns.tv_nsec) / 1e9;
// 使用 MPI_Reduce 对所有进程的 cpu_time 求和
MPI_Reduce(&cpu_time, &total_cpu_time, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if (rank == 0)
{
// 计算平均值
cpu_time = total_cpu_time / size;
}
// 将平均值广播给所有进程
MPI_Bcast(&cpu_time, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
double gflops = 1e-9 * dim * dim * dim * 2 / cpu_time;
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("%d\t: %d x %d Matrix multiply wall time : %.6fs(%.3fGflops)\n", i + 1, dim, dim, cpu_time, gflops);
fflush(stdout); // 强制刷新标准输出缓冲区
}
// 收集所有进程的局部结果到主进程
float *c = NULL;
if (rank == 0)
{
c = (float *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(float));
if (c == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed for c matrix\n");
return 0;
}
}
MPI_Gatherv(local_c, rows_per_process * dim, MPI_FLOAT, c, sendcounts, displs, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 主进程进行校验
if (rank == 0)
{
int check_row = check_indices[0];
int check_col = check_indices[1];
float result_value = c[check_row * dim + check_col];
if (fabs(result_value - check_value) > 0.001)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Verification failed at iteration %d: expected %.6f, got %.6f\n", i + 1, check_value, result_value);
}
free(c);
}
// Free memory
if (rank == 0)
{
free(a);
free(b);
}
free(local_A);
free(local_c);
free(sendcounts);
free(displs);
free(full_B);
*ave_gflops += gflops;
*max_gflops = MAX(*max_gflops, gflops);
*ave_time += cpu_time;
*min_time = MIN(*min_time, cpu_time);
}
*ave_gflops /= loop_num;
*ave_time /= loop_num;
return 1;
}
int mpi_double(int dim, int loop_num, double *ave_gflops, double *max_gflops, double *ave_time, double *min_time)
{
int rank, size;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
// Use volatile to prevent compiler optimizations
volatile double *a, *b, *local_c;
struct timespec start_ns, end_ns;
double cpu_time, total_cpu_time;
// 计算每个进程处理的行数
int rows_per_process = dim / size;
int remainder = dim % size;
if (rank < remainder)
{
rows_per_process++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < loop_num; i++)
{
int check_indices[2];
double check_value;
// 主进程分配完整矩阵内存
if (rank == 0)
{
a = (double *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(double));
b = (double *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(double));
if (a == NULL || b == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed\n");
return 0;
}
initialize_matrix_double(dim, a);
initialize_matrix_double(dim, b);
// 生成校验值
int check_row = rand() % dim;
int check_col = rand() % dim;
check_value = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < dim; k++)
{
check_value += a[check_row * dim + k] * b[k * dim + check_col];
}
check_indices[0] = check_row;
check_indices[1] = check_col;
// 广播校验行列索引和校验值
MPI_Bcast(check_indices, 2, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Bcast(&check_value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else
{
a = NULL;
b = NULL;
MPI_Bcast(check_indices, 2, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Bcast(&check_value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
// 为每个进程分配局部矩阵空间
double *local_A = (double *)malloc(rows_per_process * dim * sizeof(double));
local_c = (double *)calloc(rows_per_process * dim, sizeof(double));
if (local_A == NULL || local_c == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed\n");
return 0;
}
// 分发矩阵 A 的行到各个进程
int *sendcounts = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
int *displs = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
int offset = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < size; p++)
{
sendcounts[p] = (p < remainder) ? (rows_per_process * dim) : ((rows_per_process - 1) * dim);
displs[p] = offset;
offset += sendcounts[p];
}
MPI_Scatterv(a, sendcounts, displs, MPI_DOUBLE, local_A, rows_per_process * dim, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 所有进程都需要完整的矩阵 B
double *full_B = (double *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(double));
if (full_B == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed for full_B\n");
return 0;
}
if (rank == 0)
{
memcpy(full_B, b, dim * dim * sizeof(double));
}
MPI_Bcast(full_B, dim * dim, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
timespec_get(&start_ns, TIME_UTC);
matrix_multiply_double(dim, rank, size, local_A, full_B, local_c);
timespec_get(&end_ns, TIME_UTC);
cpu_time = (end_ns.tv_sec - start_ns.tv_sec) + (end_ns.tv_nsec - start_ns.tv_nsec) / 1e9;
// 使用 MPI_Reduce 对所有进程的 cpu_time 求和
MPI_Reduce(&cpu_time, &total_cpu_time, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if (rank == 0)
{
// 计算平均值
cpu_time = total_cpu_time / size;
}
// 将平均值广播给所有进程
MPI_Bcast(&cpu_time, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
double gflops = 1e-9 * dim * dim * dim * 2 / cpu_time;
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("%d\t: %d x %d Matrix multiply wall time : %.6fs(%.3fGflops)\n", i + 1, dim, dim, cpu_time, gflops);
fflush(stdout); // 强制刷新标准输出缓冲区
}
// 收集所有进程的局部结果到主进程
double *c = NULL;
if (rank == 0)
{
c = (double *)malloc(dim * dim * sizeof(double));
if (c == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed for c matrix\n");
return 0;
}
}
MPI_Gatherv(local_c, rows_per_process * dim, MPI_DOUBLE, c, sendcounts, displs, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 主进程进行校验
if (rank == 0)
{
int check_row = check_indices[0];
int check_col = check_indices[1];
double result_value = c[check_row * dim + check_col];
if (fabs(result_value - check_value) > 0.000001)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Verification failed at iteration %d: expected %.6f, got %.6f\n", i + 1, check_value, result_value);
}
free(c);
}
// Free memory
if (rank == 0)
{
free(a);
free(b);
}
free(local_A);
free(local_c);
free(sendcounts);
free(displs);
free(full_B);
*ave_gflops += gflops;
*max_gflops = MAX(*max_gflops, gflops);
*ave_time += cpu_time;
*min_time = MIN(*min_time, cpu_time);
}
*ave_gflops /= loop_num;
*ave_time /= loop_num;
return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int rank;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
int n = 10; // Default matrix size exponent
int loop_num = 5; // Number of iterations for averaging
double ave_gflops = 0.0, max_gflops = 0.0; // Average and maximum Gflops
double ave_time = 0.0, min_time = 1e9; // Average and minimum time
int use_double = 0; // Default to float precision
// Help message
if (argc == 1 || (argc == 2 && (strcmp(argv[1], "-h") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)))
{
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("Usage: mpiexec/mpirun [-n/-np $NUM_PROCS] %s [-n SIZE] [-l LOOP_NUM] [-float|-double]\n", argv[0]);
printf(" -n SIZE Specify matrix size, like 2^SIZE (default: 10)\n");
printf(" -l LOOP_NUM Specify number of iterations (default: 5)\n");
printf(" -float Use float precision (default)\n");
printf(" -double Use double precision\n");
printf(" -h, --help Show this help message\n");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
// Parse -n, -l, -float, -double options
int double_flag = 0, float_flag = 0;
for (int argi = 1; argi < argc; ++argi)
{
if (strcmp(argv[argi], "-n") == 0 && argi + 1 < argc)
{
n = atoi(argv[argi + 1]);
argi++;
}
else if (strcmp(argv[argi], "-l") == 0 && argi + 1 < argc)
{
loop_num = atoi(argv[argi + 1]);
argi++;
}
else if (strcmp(argv[argi], "-double") == 0)
{
double_flag = 1;
}
else if (strcmp(argv[argi], "-float") == 0)
{
float_flag = 1;
}
}
if (double_flag && float_flag)
{
if (rank == 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Cannot specify both -double and -float options.\n");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 1;
}
use_double = double_flag ? 1 : 0;
int dim = (int)pow(2, n);
if (use_double)
{
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("Using double precision for matrix multiplication.\n");
}
if (!mpi_double(dim, loop_num, &ave_gflops, &max_gflops, &ave_time, &min_time))
{
MPI_Finalize();
return 1;
}
}
else
{
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("Using float precision for matrix multiplication.\n");
}
if (!mpi_float(dim, loop_num, &ave_gflops, &max_gflops, &ave_time, &min_time))
{
MPI_Finalize();
return 1;
}
}
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("Average Gflops: %.3f, Max Gflops: %.3f\n", ave_gflops, max_gflops);
printf("Average Time: %.6fs, Min Time: %.6fs\n", ave_time, min_time);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
为了确保合并之后的矩阵没有错误,主程序中增加了随机坐标校验机制。